Unlocking the Chill: Exploring Metabolism and Thermogenesis
As the temperature drops and winter settles in, our bodies partake in an remarkable dance—an intricate interplay of biochemical processes that power our very existence. At the heart of this seasonal shift lies metabolism,the engine that fuels our every movement,and thermogenesis,the interesting mechanism through which our bodies generate heat. While we often picture cozy blankets and steaming cups of cocoa in winter, beneath the surface, a symphony of cellular activity is at play, ensuring that we remain warm and vibrant. This article delves into the science behind metabolism and thermogenesis, unraveling how our bodies adapt to cold climates, the energy dynamics that govern our daily lives, and the profound implications for health and well-being. Join us on a journey through the chilly realms of human biology, where understanding the warmth within can reveal much about our resilience and vitality.
Understanding the Science of Metabolism and Its Impact on Weight Management
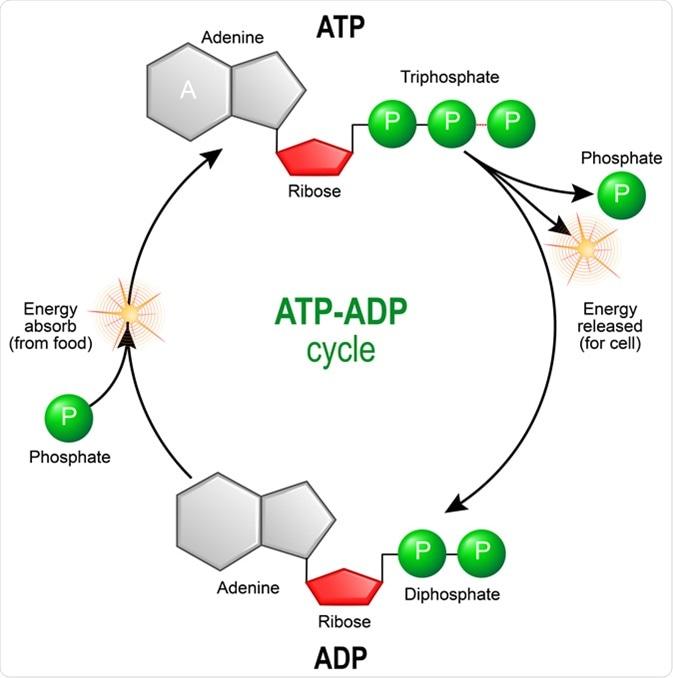
Metabolism is a complex biochemical process that maintains the delicate balance of energy within the body. It encompasses the myriad of chemical reactions that convert the food we consume into energy,allowing us to perform daily functions,exercise,and sustain vital physiological processes. The rate at which thes reactions occur is influenced by various factors, including genetics, age, and hormonal levels. Understanding these elements can provide crucial insights into weight management and overall health.
At its core, metabolism can be broken down into two major components: catabolism and anabolism. Catabolism refers to the breakdown of molecules to obtain energy, often resulting in the release of heat, while anabolism involves building up complex molecules from simpler ones, storing energy in the process.This balance between catabolic and anabolic processes considerably influences our basal metabolic rate (BMR), which is the amount of energy expended while at rest. Factors that can alter BMR include:
- muscle Mass: More muscle increases metabolic rate.
- Age: Metabolism generally slows with age.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormones like thyroid hormones can accelerate or slow metabolism.
Thermogenesis is another vital component relating to metabolism, particularly when discussing how the body generates heat. This energy expenditure can be stimulated by various factors such as physical activity, dietary intake, and even environmental temperature.there are several forms of thermogenesis, including:
- Exercise-Induced Thermogenesis: The increase in metabolism following physical activity.
- Diet-Induced Thermogenesis: The energy required for digestion and absorption of food.
- Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT): Energy expended during non-exercise movements like fidgeting.
to better illustrate the relationship between metabolism, thermogenesis, and their roles in weight management, consider the following table:
| Factor | Effect on Metabolism |
|---|---|
| Increased Muscle Mass | Boosts BMR, leading to higher daily caloric expenditure. |
| Aging | Decreases BMR, making weight management more challenging. |
| Caloric Deficit | Can decrease metabolism over time as body adapts. |
| High-Intensity Exercise | Significantly increases thermogenesis during and post-exercise. |
The Role of Thermogenesis in Caloric Expenditure and Energy Regulation
Thermogenesis plays a crucial role in the body’s ability to regulate energy expenditure and maintain homeostasis. This physiological process involves the production of heat, primarily through non-shivering thermogenesis (NST) and shivering thermogenesis. NST, mostly occurring in brown adipose tissue, is a fascinating adaptation that allows the body to burn calories without physical exertion, thereby contributing significantly to overall metabolic rate. The body’s ability to generate heat in response to cold exposure not only aids in thermoregulation but also plays a role in weight management by increasing caloric burn.
Along with its basic role in heat generation, thermogenesis is influenced by several factors that can enhance or inhibit its effectiveness. Key influencers include:
- Dietary composition: Thermic effect of food (TEF) varies with macronutrients; proteins tend to elicit a higher thermogenic response compared to fats and carbohydrates.
- Physical activity: Exercise increases metabolic rates during and after activity, stimulating both shivering and non-shivering thermogenesis.
- Hormonal balance: Hormones such as thyroid hormones and catecholamines are essential regulators of metabolic processes, including thermogenesis.
- Environmental temperature: Exposure to cold environments can trigger increased thermogenic activity, stimulating energy expenditure.
The body’s regulation of energy expenditure through thermogenesis can be displayed in a simplified manner, emphasizing the balance between caloric intake and expenditure:
| Components | Function |
|---|---|
| Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) | energy required for basic bodily functions. |
| Physical Activity | Energy used during exercise and movement. |
| Thermogenesis | heat production leading to increased caloric expenditure. |
Ultimately, understanding the mechanics of thermogenesis is essential for those aiming to achieve optimal health and fitness goals. By recognizing the interplay of diet, physical activity, hormonal influences, and environmental factors, individuals can effectively manipulate their caloric expenditure. Embracing strategies that enhance thermogenic processes may pave the way for improved energy balance, facilitating weight maintenance and metabolic health.
Foods and Rituals to Boost Metabolic Rate Naturally
Embracing a diet rich in thermogenic foods is a straightforward way to enhance your metabolic rate. These foods require more energy to digest and process, effectively boosting calorie expenditure.Consider incorporating the following items into your meals:
- Lean Proteins: Chicken, turkey, fish, and legumes can elevate the thermic effect of food (TEF) due to their high protein content.
- Green Tea: Packed with catechins, this drink not only hydrates but also stimulates fat oxidation and increases energy expenditure.
- Chili Peppers: The capsaicin in peppers can temporarily raise your metabolic rate, while also adding a flavorful kick to your dishes.
- Whole Grains: Oats, quinoa, and brown rice digest slowly, providing sustained energy and boosting metabolism over time.
Rituals can play a vital role in igniting metabolic fire. Start your day with a refreshing glass of cold water; this simple act stimulates your body and prepares it for the caloric challenge ahead. Furthermore, establishing a routine that incorporates periodic strength training can build lean muscle mass, which is more metabolically active than fat tissue. Schedule your workouts or mimic a robust routine at home to enhance metabolic rates even during rest.
Engaging in mindful eating helps reconnect with your body’s natural hunger cues. Take the time to savor every bite, and pay attention to portion sizes. Not only do these practices promote better digestion, but they also prevent overeating, allowing your body to effectively utilize the calories it takes in. Consider a dining ritual that involves eating without distractions to allow your body to signal when it’s satiated.
Lastly, integrating natural supplements such as ginger and cinnamon into your culinary repertoire can be beneficial. These ingredients are known for their potential to improve blood circulation and act as thermogenic agents. To help visualize this, see the table below for a speedy comparison of some beneficial foods and their metabolic advantages:
| Food Item | Metabolic Benefit |
|---|---|
| lean Meat | High TEF, builds muscle |
| Green Tea | Increases fat oxidation |
| Chili Peppers | Boosts calorie burn |
| Whole Grains | Sustained energy release |
| Ginger | Improves circulation |
Practical Strategies for enhancing Thermogenic Response during Winter Months
As the temperatures drop, it’s imperative to adopt specific habits that can boost thermogenesis, allowing your body to generate heat more efficiently. One effective strategy is to incorporate more high-intensity interval training (HIIT) into your fitness routine. This type of exercise elevates your metabolic rate not only during the workout but also for several hours afterward. You can start with short bursts of intense activity,followed by brief recovery periods,to stimulate your thermogenic response.
another approach is to reassess your dietary habits. Consuming foods that are rich in protein, such as lean meats, legumes, and dairy, can increase the thermic effect of food (TEF). High-fiber foods, like fruits and vegetables, can enhance digestion and thermogenesis. Consider including the following thermogenic foods in your meals:
- Chili Peppers: Contain capsaicin, which boosts metabolism.
- Green Tea: Rich in catechins that enhance fat oxidation.
- Coconut Oil: Contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) that elevate metabolism.
- Ginger: Can increase thermogenic response through its warming properties.
Don’t underestimate the power of temperature manipulation in your habitat. Keeping your living space slightly cooler can push your body to expend more energy to maintain its core temperature. Adding layers, such as wearing thermal clothing or cozy blankets, can help. Engaging in exposure to cold, whether through taking cold showers or brave outdoor excursions, is another way to harness the body’s innate thermogenic mechanisms. The table below outlines simple activities and their thermal impacts:
| Activity | Thermogenic Effect |
|---|---|
| Cold Showers | Stimulates brown fat activation |
| Outdoor Walk in Cold | Increases calorie burning |
| Using a Sauna | Promotes sweat and calorie burn |
| Winter Sports | Engages multiple muscle groups |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Metabolism & Thermogenesis
Q1: What exactly is metabolism?
A1: Metabolism is the body’s intricate biochemical dance, encompassing all the chemical reactions that turn food into energy.It is divided into two main components: catabolism, where substances are broken down to release energy, and anabolism, where energy is used to build and repair tissues. Think of it as the body’s power plant—converting nutrients into the energy we need to thrive.
Q2: How does thermogenesis fit into the metabolism puzzle?
A2: Thermogenesis is the heat production that occurs during metabolism. Essentially, it’s how your body generates heat to maintain its core temperature. This process is crucial for survival,especially in colder environments. It can be categorized into three types: basal thermogenesis (energy expended at rest), adaptive thermogenesis (adjustments in response to environmental changes), and exercise-induced thermogenesis (calories burned during physical activity).
Q3: Can you explain how our bodies regulate thermogenesis?
A3: Absolutely! The body regulates thermogenesis through a complex interplay of hormones,nervous system signals,and various tissues,particularly brown adipose tissue. When temperatures drop or you consume certain foods, your body activates mechanisms to increase heat production. As a notable example, hormones like thyroxine from the thyroid and norepinephrine from the adrenal glands can ramp up energy expenditure and heat generation.
Q4: Is all thermogenesis the same?
A4: not quite! There are different pathways and tissues involved. Brown adipose tissue is a key player in non-shivering thermogenesis, which is particularly adept at burning calories to produce heat without the muscle contractions of shivering. White adipose tissue, traditionally associated with fat storage, can also contribute to thermogenesis under specific conditions, notably through a process called “browning.”
Q5: What role does diet play in metabolism and thermogenesis?
A5: Your diet isn’t just a source of fuel; it shapes your metabolic processes too! Nutrients, especially protein, can increase thermogenesis in what’s known as the thermic effect of food (TEF). This means that digesting and metabolizing food requires energy—roughly 10% of your total calorie intake! Spicy foods, like those containing capsaicin, can also boost thermogenesis temporarily. Ultimately, a balanced diet supports a robust metabolism and encourages efficient thermogenesis.
Q6: Can I boost my thermogenesis and metabolism?
A6: Yes, you can! Incorporating regular physical activity, particularly strength training and high-intensity interval workouts, can enhance muscle mass and elevate your resting metabolic rate. additionally, consuming a diet rich in whole foods, staying adequately hydrated, and getting enough sleep can all contribute positively to your metabolism. some even advocate for cold exposure (like cold showers) to stimulate thermogenesis!
Q7: are there any myths about metabolism and thermogenesis that need dispelling?
A7: Certainly! One prevalent myth is that metabolism is solely persistent by genetics and that it cannot be changed. While genetics do play a role, lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, and sleep significantly influence metabolic rates. another myth is that crash diets can effectively boost metabolism—such drastic measures can actually slow it down! Enduring changes are key to maintaining a healthy metabolic rate and efficient thermogenesis.
Q8: How do aging and metabolism relate?
A8: As we age, our metabolism tends to slow down due to muscle loss and hormonal changes, which can impact thermogenesis as well. However, engaging in regular physical activity, especially strength training, can help counteract these effects. It’s all about keeping that body engaged and active, like a well-tuned engine ready to generate energy and heat.
In a world where our bodies are in constant flux, understanding metabolism and thermogenesis empowers us to make informed choices for our health. Whether through nutrition, exercise, or lifestyle adjustments, we hold the keys to optimize our body’s energy balance.
In Summary
In closing, the interplay between metabolism and thermogenesis offers a captivating glimpse into the complexity of our body’s inner workings. From the metabolic machinery that fuels our daily activities to the intricate processes that regulate heat production, understanding these dynamics illuminates the fascinating ways in which we engage with our environment. As we continue to explore the depths of human physiology, it becomes clear that our bodies are not just passive systems, but active participants in the dance of energy regulation. So, whether you’re contemplating a new workout regime or simply curious about how your body responds to the changing seasons, remember that the journey of metabolism and thermogenesis is as dynamic as life itself—a perpetual cycle of energy transformation that keeps us warm and vibrant. Embrace the science, and let it inspire you to foster a deeper connection with your own physiology. 🌡️