The Gut-Brain Connection: How Your Microbiome Affects Your Mood
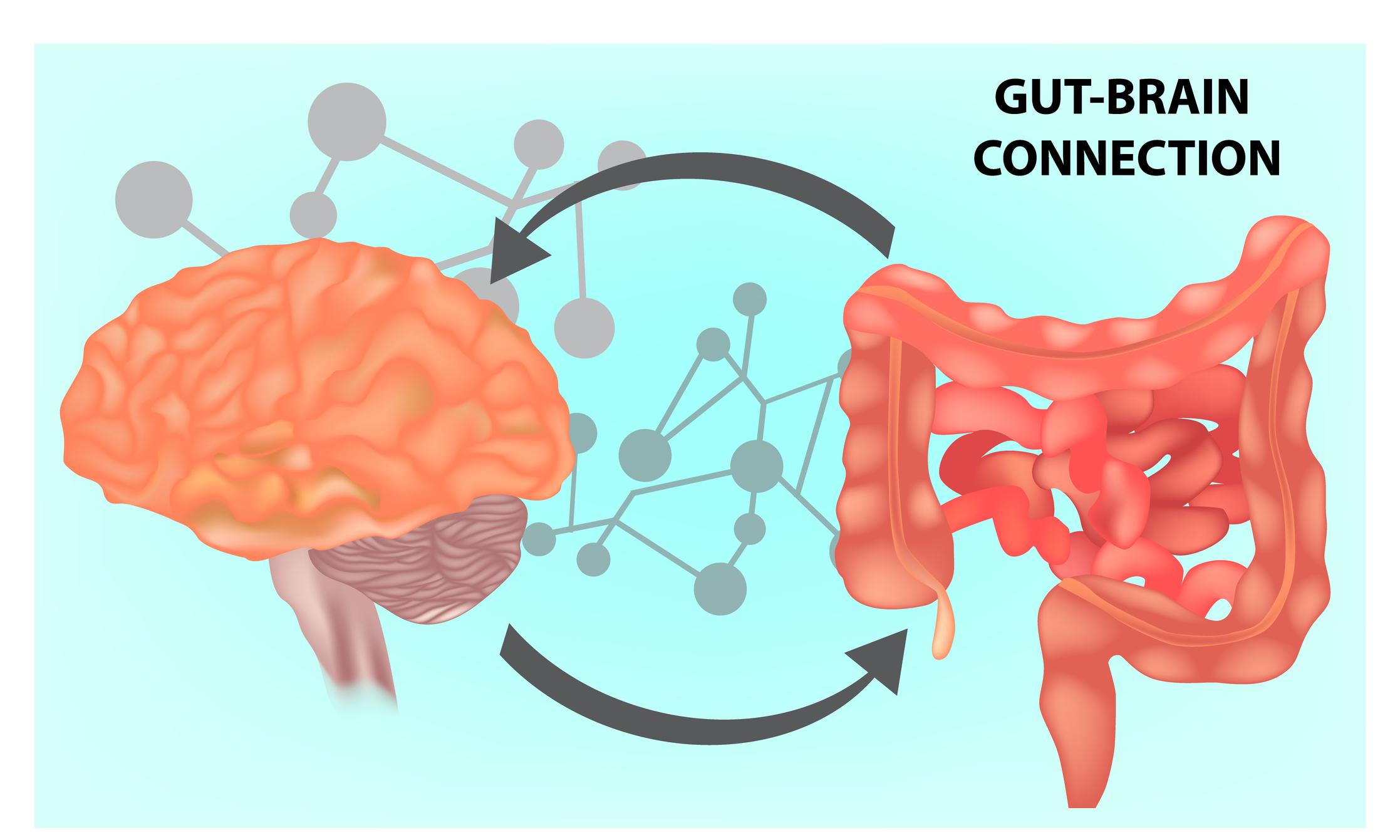
In the intricate web of the human body, few connections are as remarkable as the one between our gut and our brain. This relationship, often referred to as the gut-brain connection, unveils a fascinating dialog where bacteria, emotions, and mental well-being intertwine. recent scientific advancements have shed light on the unusual role our microbiome plays not just in digestion, but also in shaping our mood and emotional health. As we delve into this dynamic interplay, we’ll uncover how tiny microorganisms residing in our digestive system can influence our thoughts, feelings, and overall mental state. Join us on a journey through this complex landscape, where understanding the gut-brain connection may pave the way for new approaches to fostering emotional resilience and mental clarity. 🧠💚
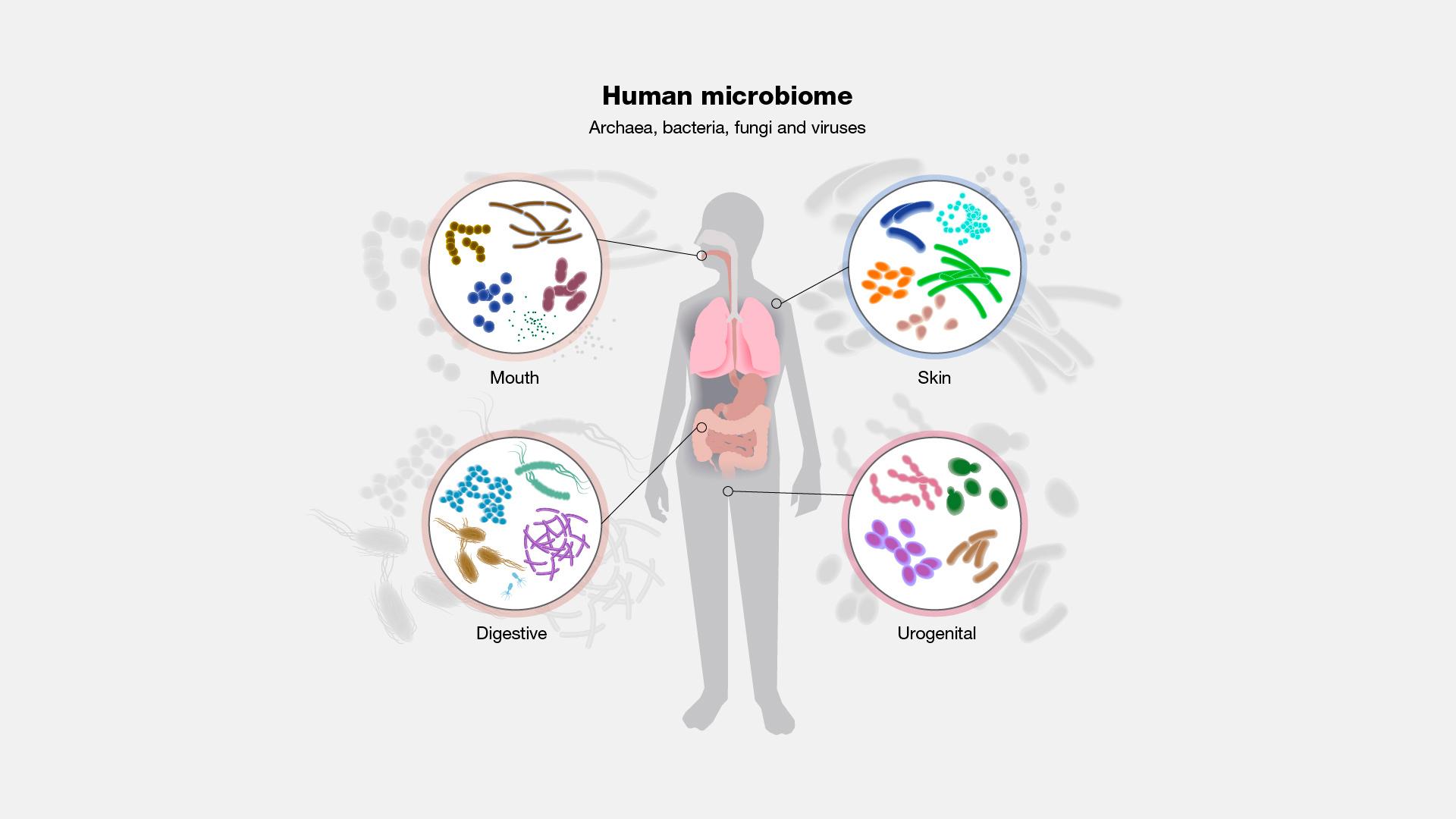
Understanding the Microbiome: The Body’s Hidden Ecosystem
The microbiome is a complex community of microorganisms residing in various parts of your body, with the gut being the most notable habitat. This hidden ecosystem plays a crucial role in our overall health, especially when it comes to influencing our mood and mental well-being. Research indicates that a healthy gut microbiome can produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which is essential in regulating mood. Furthermore, the gut and brain communicate through the gut-brain axis, a dynamic relationship that allows emotional and cognitive functions to be influenced by the state of our intestinal flora. Key factors that support a thriving microbiome include:
- Diverse diet: Consuming a varied selection of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains keeps the microorganisms in your gut happy and diverse.
- Probiotics: Almost like friendly reinforcements, foods like yogurt and fermented foods can enhance the population of beneficial bacteria.
- Prebiotics: These are fibers that nourish good bacteria, found in foods like garlic, onions, and bananas.
Moreover, the influence of the microbiome extends beyond mood regulation; it affects cognitive processes, including memory and learning.An imbalance in gut bacteria, often referred to as dysbiosis, can lead to conditions such as anxiety and depression.Research is uncovering fascinating correlations between the gut microbiota and various mental health conditions, suggesting that improving gut health could be a new frontier in mental health treatment. To illustrate this connection, here’s a brief overview of common mood disorders and their potential links to gut health:
| Mood disorder | Microbiome Impact |
|---|---|
| Depression | Lower levels of beneficial bacteria. |
| Anxiety | Higher levels of inflammation markers. |
| Bipolar disorder | Altered gut flora diversity. |
The Science of Mood Regulation: How Gut Bacteria Influence Emotions
The human body hosts trillions of microorganisms, with gut bacteria playing a pivotal role in regulating mood and emotions. Research has increasingly pointed to the gut-brain axis, a dialogue network linking our gastrointestinal system and the brain. This connection reveals how gut health can profoundly affect emotional states. For instance, certain bacteria produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, often dubbed the ”feel-good” chemical. an imbalance in gut flora can lead to a decrease in serotonin levels, contributing to feelings of anxiety and depression.
Moreover, the diet we choose directly influences our gut microbiome composition. Foods rich in prebiotics and probiotics can foster a healthy microbial environment that supports mood regulation. Consuming a varied diet that includes: Gut-Brain
- Fermented foods (yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut)
- Fiber-rich foods (whole grains, fruits, vegetables)
- Omega-3 fatty acids (fish, flaxseeds, walnuts)
can promote healthier gut bacteria and perhaps improve emotional well-being. Understanding this intricate connection underscores the importance of maintaining gut health not only for digestive wellness but also for emotional resilience.
nourishing Your Gut: dietary Strategies for a Happier Mind
To cultivate a healthy gut microbiome, it’s essential to balance your diet with a range of nutrient-dense foods. Emphasizing fermented foods can introduce beneficial bacteria to your system, promoting gut health and, in turn, enhancing your mental well-being. Incorporate the following sources into your meals:
- Kefir – A tangy,fermented dairy product rich in probiotics.
- Kimchi – Spicy and fermented vegetables packed with nutrients and flavor.
- Sauerkraut – Fermented cabbage that adds crunch and health benefits to your diet.
- Tempeh – A fermented soy product that serves as a protein-rich meat choice.
In addition to fermented foods, focusing on fiber-rich options supports gut diversity, which is crucial for a healthier microbiome. The following foods can enhance your fiber intake:
| Food | Fiber Content (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Chia Seeds | 34g |
| Lentils | 8g |
| Brussels Sprouts | 3g |
| Oats | 10g |
By incorporating both fermented and fiber-rich foods into your diet, you pave the way for a flourishing gut microbiome. This harmonious balance not only nurtures a healthier digestive system but also lays the groundwork for a happier, more resilient mind.
The Mind-Gut Link: Practical tips for Enhancing Mental Wellness
the intricate relationship between our gut and our mind offers a wealth of opportunities for enhancing mental wellness. By focusing on specific lifestyle choices and dietary habits, we can promote a balanced microbiome that not only nourishes our body but also supports our emotional state. Consider incorporating the following practical strategies into your routine to help strengthen this powerful connection:
- Probiotic-Rich Foods: Include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi in your diet to boost beneficial gut bacteria.
- Eat Prebiotics: Incorporate foods such as garlic, onions, and bananas to nourish your existing gut flora.
- Minimize Processed Foods: Reduce sugar and refined carbs which can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water supports digestion and promotes a healthy microbiome.
- Mindful Eating: take time to enjoy meals, reducing stress and improving gut function.
Moreover,incorporating regular physical activity and stress-reducing practices can further enhance your gut-brain connection. Aiming for at least 30 minutes of exercise a day can stimulate gut health while boosting endorphins, leading to improved mood and anxiety levels.Complement these practices with relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, which not only calm the mind but also support a healthier digestive system. Below is a simple reminder table to help you keep track of your gut-friendly habits: Gut-Brain
| Habit | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Probiotic Intake | Daily |
| Hydration | 8 glasses/day |
| Exercise | 5 times/week |
| Meditation | 10 minutes/day |
Final Thoughts
the intricate dance between our gut microbiome and mental wellbeing is a fascinating testament to the complexity of human health. As we unravel the threads of this gut-brain connection, it becomes increasingly clear that what we eat, how we nurture our microbiome, and our overall lifestyle choices can have profound implications on our mood and mental clarity. Gut-Brain
This emerging field of research invites us to take a holistic view of health—recognizing that our gut is not merely a digesting organ but a vibrant ecosystem that influences our emotions and cognitive function.As we continue to explore this symbiotic relationship, we open doors to new possibilities for mental health treatments and nutritional strategies. Gut-Brain
So, the next time you savor a meal or face a challenging day, remember: the symphony of microbes within your gut may just be conducting the rhythms of your mind. Embrace the connection, nurture it wisely, and let it guide you toward a healthier, more balanced life. After all, in the complex tapestry of health, every thread counts—especially those woven by the microbes that call our gut home. 🧠💚 Gut-Brain